Hello दोस्तों! आज हम C Programming का सबसे important और basic concept सीखने जा रहे हैं। अगर आप C Programming सीख रहे हैं, तो आपको Data Type को समझना बहुत ज़रूरी है।
अक्सर beginners को confusion होता है कि int, float, या char कब use करना है। आज के इस लेख हम C में Data Type को बहुत ही आसान शब्दों में समझेंगे कि Data Type in C in Hindi क्या है, इनका size क्या होता है, और इन्हें program में कैसे use करते हैं।
इस article को पढ़ने के बाद आप interview और exams में Data Types से जुड़े किसी भी सवाल का जवाब आसानी से दे पाएंगे। तो चलिए शुरू करते हैं!
Table of Contents
1. C Language में Data Type क्या होता है?
Programming शुरू करने से पहले एक real-life example लेते हैं। सोचिए हमारे किचन में अलग-अलग डिब्बे (containers) हैं।
- चीनी रखने के लिए अलग डिब्बा है।
- नमक के लिए अलग है।
- पानी रखने के लिए बोतल है।
हम चीनी के डिब्बे में पानी नहीं रखते, है न? बिल्कुल वैसे ही Programming में Data (values) को store करने के लिए अलग-अलग तरह के containers चाहिए होते हैं।
Data Type का आसान मतलब
C में Data Type का मतलब है – Data का प्रकार। जब हम C Language में कोई Variable बनाते हैं, तो हमें Compiler को पहले ही बताना पड़ता है कि उस Variable में हम किस तरह का Data store करने वाले हैं। क्या वो एक number होगा? क्या वो point (decimal) वाला number होगा? या कोई alphabet होगा?
C Programming में Data Type क्यों ज़रूरी है?
C एक Statically Typed Language है। इसका मतलब है कि C language बहुत strict है।
- Memory Allocation: Compiler को पता होना चाहिए कि data store करने के लिए computer की memory (RAM) में कितनी जगह (bytes) बचानी है।
- Operation Decision: Compiler को यह भी पता चलता है कि उस data पर कौन से math operations (जैसे +, -, *) किए जा सकते हैं।
बिना Data Type के Program क्यों नहीं चलता?
अगर हम data type नहीं बताएंगे, तो computer confuse हो जाएगा। उसे समझ नहीं आएगा कि जो 10 हमने लिखा है, वो एक number है या सिर्फ text। इसलिए C में variable बनाने से पहले Data Type लिखना mandatory (अनिवार्य) है।
2. C Language में Data Types के प्रकार
C Language में Data Types को मुख्य रूप से 3 categories में बांटा गया है। इसे समझने के लिए नीचे दी गई Table देखें:
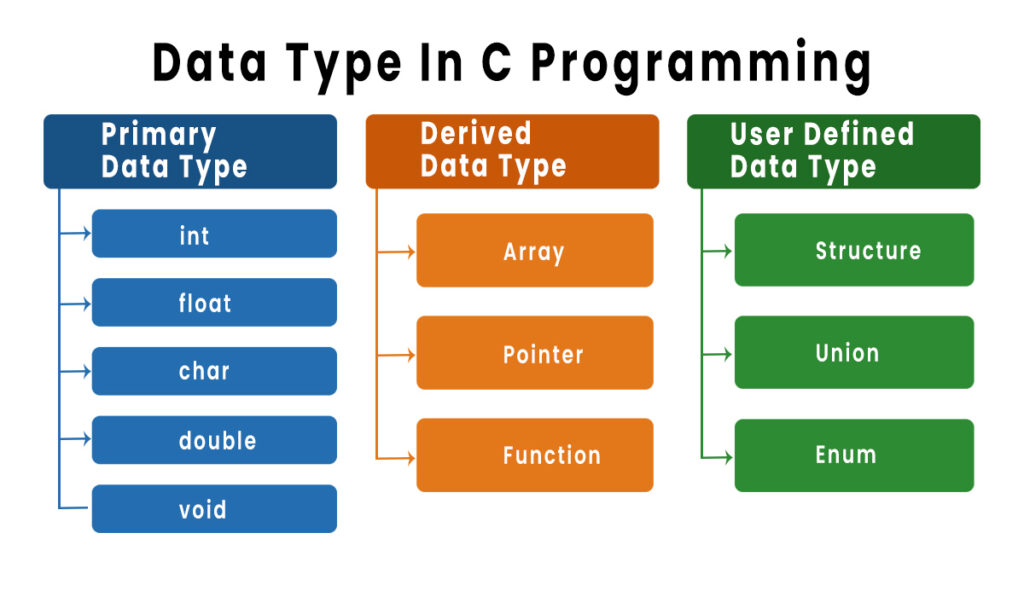
C Language में कुल कितने Data Types होते हैं?
| Category | Data Types | Description |
| Primary (Basic) | int, char, float, double, void | ये सबसे basic types हैं जो numbers और characters store करते हैं। |
| Derived | Array, Pointer, Function | ये Primary types की मदद से बनते हैं। |
| User Defined | Structure, Union, enum | ये programmer अपनी ज़रूरत के हिसाब से define करते है। |
3. Basic Data Types in C (Primitive Data Types)
C में Basic Data Type बहोत Important है इस लिये, चलिए एक-एक करके सबको समझते हैं।
int Data Type in C
int का मतलब है Integer। इसका use तब होता है जब हमें बिना दशमलव (decimal) वाले numbers store करने हों।
- Meaning: Whole numbers (पूर्ण संख्याएं)
- Size: आमतौर पर 2 bytes या 4 bytes (Compiler पर depend करता है, आज कल के systems में 4 bytes).
- Format Specifier: %d
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age = 25; // यहाँ age एक integer variable है
printf("My age is: %d", age);
return 0;
}
Output:
My age is: 25
char Data Type in C
char का मतलब है Character। जब हमें कोई Single Alphabet या Special Symbol store करना हो, तो char का use होता है। इसे हमेशा single quotes ‘ ‘ में लिखा जाता है।
- Memory Size: 1 byte
- Format Specifier: %c
ASCII Concept: Computer ‘A’ या ‘B’ नहीं समझता। वो हर character को एक number (ASCII Value) में बदल देता है। जैसे ‘A’ की value 65 होती है।
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char section = 'A';
printf("Your class section is: %c", section);
return 0;
}
Output:
Your class section is: A
float Data Type in C
float का use तब होता है जब हमें दशमलव (Decimal) वाले numbers store करने होते हैं।
- Meaning: Floating point numbers.
- Precision: यह point के बाद 6 digits तक value सही दे सकता है।
- Size: 4 bytes
- Format Specifier: %f
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float price = 99.50;
printf("Price is: %f", price);
return 0;
}
Output:
Price is: 99.500000
double Data Type in C
double भी दशमलव (decimal) values store करता है, लेकिन यह float से दुगना (double) size और accuracy देता है।
- Use-case: जब scientific calculations करनी हों जहाँ बहुत बारीकी (high precision) की ज़रूरत हो।
- Size: 8 bytes
- Format Specifier: %lf (long float)
4. Data Type In C Size & Range Table With Format Specifier
यह Table bahot Useful है इसे याद रखना बहोत Useful होता है! (नोट: Size compiler के अनुसार थोड़ा बदल सकता है, पर यह standard है)।
| Data Type | Size (Bytes) | Range (Value Limit) | Format Specifier |
| char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 | %c |
| int | 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | %d |
| float | 4 bytes | 1.2E-38 to 3.4E+38 | %f |
| double | 8 bytes | 2.3E-308 to 1.7E+308 | %lf |
| void | 0 | Valueless | – |
5. Derived Data Types in C
Derived Data Types वो होते हैं जो Primary Data Types (int, char, float) से मिलकर बनते हैं। इसमें मुख्य रूप से Array, Pointer, और Function आते हैं।
Array Data Type in C
अगर हमें एक ही जैसे 50 students के marks store करने हों, तो क्या हम 50 variable बनाएंगे? (int s1, s2, s3…) नहीं! Array एक ऐसा variable है जो एक ही नाम के अंदर एक ही type के बहुत सारे values store कर सकता है।
Simple Example:
int marks[5] = {90, 85, 70, 95, 88};
// marks[0] prints 90
Pointer Data Type in C
Pointer का नाम सुनकर डरना नहीं है। आसान भाषा में, Pointer एक ऐसा variable है जो किसी दूसरे variable का Address (memory location) store करता है, उसकी value नहीं।
- इसका इस्तेमाल memory management में होता है।
Example:
int x = 10;
int *ptr = &x; // ptr ab x का Address Hold कर रहा है।
Function Data Type in C
Function भी एक Derived Data Type है। यह निर्देशों (code) का एक ऐसा group होता है जो एक specific काम करता है। इसे Derived इसलिए कहते हैं क्योंकि इसका return type (जैसे int, void) Primary Data Type पर depend करता है।
Example:
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b; // यह int value return करेगा
}
6. User Defined Data Types in C (Structure, Union, Enum)
User Defined Data Types वो होते हैं जिन्हें हम अपनी ज़रूरत के हिसाब से खुद define करते है।
Structure (struct) Data Type in C
Structure (struct) हमें अलग-अलग Data Types के variables को एक single name के अंदर group करने की सुविधा देता है।
- ज़रूरत: Real-world entities (जैसे एक Student, Book या Car) की information store करने के लिए, जहाँ data अलग-अलग प्रकार का हो सकता है।
- उदाहरण: एक Student के लिए हमें int id, char name, और float marks तीनों चाहिए।
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
// Structure define karna
struct Student {
int id;
float marks;
char grade;
};
int main() {
// Structure variable banana
struct Student s1;
s1.id = 101;
s1.marks = 88.5;
s1.grade = 'A';
printf("Student ID: %d, Marks: %.1f\n", s1.id, s1.marks);
return 0;
}
Output:
Student ID: 101, Marks: 88.5
Union Data Type in C
Union Structure जैसा ही होता है, लेकिन इसमें सबसे बड़ा अंतर यह है कि Union के सभी members एक ही Memory Location को share करते हैं।
- फायदा: इससे Memory Optimize (बचाई) जा सकती है, खासकर जब हमें पता हो कि एक time पर Union का केवल एक ही member use होगा।
- Memory Size: Union का size उसके सबसे बड़े member के size के बराबर होता है।
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
// Union define karna
union Data {
int i;
float f;
char str[20]; // Sabse bada member
};
int main() {
union Data d;
// Sirf ek time par ek hi value store hogi
d.i = 10;
printf("Integer: %d\n", d.i); // Output: 10
d.f = 220.5;
printf("Float: %.1f\n", d.f); // Integer value corrupt ho jayegi
return 0;
}
Output:
Integer: 10
Float: 220.5
Enumeration (enum) Data Type in C
enum क्या होता है?
enum (Enumeration) एक user-defined data type है। इसका use तब होता है जब हम numbers को English Names देना चाहते हैं ताकि code पढ़ने में आसान हो जाए। C Compiler इन names को automatically integer values (0, 1, 2…) assign कर देता है।
enum का Real Life Example
हफ्ते के दिनों के लिए हम 0, 1, 2 की जगह Mon, Tue, Wed use कर सकते हैं।
enum Week {Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, Sun};
int main() {
enum Week today;
today = Wed;
printf("%d", today); // Output: 2 (kyunki Mon=0, Tue=1, Wed=2)
return 0;
}
7. Void Data Type in C
void का मतलब
void का हिंदी मतलब होता है खाली या शून्य। इसका अपना कोई size नहीं होता।
void function क्या होता है?
जब कोई function कोई value return नहीं करता, तो हम उसे void declare करते हैं। Example: void main() का मतलब है कि main function कुछ भी return नहीं करेगा।
8. Data Type vs Variable
बहुत से Beginners “Data Type” और “Variable” में confuse हो जाते हैं। चलिए इसे clear करते हैं।
| Feature | Data Type | Variable |
| Definition | यह बताता है कि data किस तरह का है (Type)। | यह उस data को store करने वाले container का नाम है (Name)। |
| Example | int, float, char | age, salary, grade |
| Role | यह memory का size decide करता है। | यह memory location को identify करता है। |
| Simple Words | यह “डिब्बा किस चीज़ का है” (e.g., steel का डिब्बा)। | यह “डिब्बे पर लिखा नाम” है (e.g., चीनी का डिब्बा)। |
Syntax: Data_Type Variable_Name; (e.g., int salary;)
9. Common Mistakes (Beginner Errors)
C Programming सीखते समय ये गलतियाँ कभी मत करना:
- Wrong Format Specifier: int के लिए %f लगा देना। इससे output गलत आएगा।
- Memory Overflow: int की range से बड़ा number उसमें store करने की कोशिश करना। (e.g., Phone number को int में डालना गलत है, उसके लिए long long चाहिए)।
- float Precision Error: float कभी-कभी exact comparison (==) में fail हो जाता है क्योंकि वो approximate value store करता है।
- Character Confusion: ‘5’ एक character है, जबकि 5 एक integer number है। दोनों अलग हैं।
10. Data Type In C Quizzes
Q1. अगर हमें किसी वस्तु का वज़न (Weight) store करना है जो decimal में हो सकता है (जैसे 75.5 kg), तो C language में कौन सा basic data type use करेंगे?
A) int B) float C) char D) void
float data type decimal (floating point) values store करने के लिए use होता है। int केवल whole numbers के लिए होता है।Q2. निम्न में से कौन सा Data Type, C language में Derived Data Type की category में आता है?
A) int B) Structure C) Pointer D) enum
int primary है जबकि Structure और enum user-defined हैं।Q3. C Programming में char data type का standard memory size कितना होता है?
A) 2 bytes B) 4 bytes C) 1 byte D) 8 bytes
char data type एक ASCII character store करता है और इसका size हमेशा 1 byte होता है।Q4. Structure और Union में वह कौन सा मुख्य अंतर है जिसकी वजह से Union memory optimize करता है?
A) Union के सभी members एक ही memory location share करते हैं B) Structure के members access नहीं किए जा सकते C) Structure का size हमेशा सबसे बड़े member के बराबर होता है D) Union primary data type होता है
Q5. C language में void data type का मुख्य उपयोग क्या है?
A) Zero size integer declare करना B) Compiler को memory optimize करने का संकेत देना C) Function के return type के रूप में जब कोई value return न हो D) High precision decimal values store करना
void का मतलब होता है “कोई value नहीं”, इसलिए इसका use उन functions में होता है जो कोई value return नहीं करते।11. FAQs
Q1. Data type in C क्या होता है?
Ans: Data type in C यह बताता है कि कोई variable किस तरह का data (number, character, decimal आदि) store करेगा और memory में कितनी जगह लेगा।
Q2. C language में सबसे ज़्यादा use होने वाला data type कौन सा है?
Ans: int (integer) सबसे ज्यादा use होने वाला data type है क्योंकि programming में counting, loops और calculations के लिए numbers की जरूरत सबसे ज्यादा होती है।
Q3. int और float data type में क्या difference है?
Ans: int बिना decimal point वाले numbers store करता है (जैसे 10, 20)।
float decimal point वाले numbers store करता है (जैसे 10.5, 20.99)।
Q4. Data type का size कैसे पता करें?
Ans: किसी भी data type का size जानने के लिए sizeof() operator का उपयोग किया जाता है।
Example: sizeof(int)
Q5. क्या C language में boolean data type होता है?
Ans: पुराने C versions (C89/C90) में boolean data type नहीं होता था। उस समय 0 को false और 1 को true माना जाता था।
C99 standard के बाद <stdbool.h> header file include करके bool data type का use किया जा सकता है।
Q6. void data type का use कब होता है?
Ans: void data type का use मुख्य रूप से functions के साथ किया जाता है जब function को कोई value return नहीं करनी होती है।
12. Conclusion निष्कर्ष)
तो दोस्तों, आज हमने सीखा कि Data Type in C in Hindi क्या है और यह C Programming की नींव (foundation) क्यों है।
- Numbers के लिए int use करें।
- Decimal (point) numbers के लिए float या double use करें।
- Characters के लिए char use करें।
- User Defined Data Types (Struct, Union) से आप Complex Data को आसानी से Organize कर सकते हैं।
- Data types सही चुनने से आपका program fast चलता है और memory waste नहीं होती।
अगर आप एक अच्छे Programmer बनना चाहते हैं, तो इन data types के साथ code लिखकर practice जरूर करें। अगर आपको कोई doubt है तो नीचे comment करें!
