Welcome Anwarcodes!
आज के इस Post हम बात करेंगे C Language में Data Conversion के बारे में Data Conversion भी एक बहोत जरुरी topic है, अगर आप C Programming सीख रहे हैं तो ये Post आपके लिए बहोत Useful होने वाला है।
इस पोस्ट में, आप सीखेंगे कि C Language में Data Conversion क्या है, इसके दो मुख्य प्रकार—Implicit और Explicit—कैसे काम करते हैं, और हम Type Casting का उपयोग करके अपने Program को कैसे कंट्रोल और सही Calculation कर सकते हैं।
Table of Contents
1. C Language में Data Conversion क्या है?
C Language में Data Conversion एक प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा एक Data Type (Source) की Value को दूसरे Data Type (Target) की Value में बदला जाता है। इस पूरे Concept को अक्सर Type Casting भी कहा जाता है।
2. Data Conversion के Types in C
C Language में Data Conversion मुख्य रूप से दो तरह का होता है:
3.1 Implicit Type Conversion
Implicit Type Conversion तब होता है जब Compiler अपने आप एक Data Type को दूसरे Data Type में बदल देता है।
- यह कब होता है?
जब एक Expression में अलग-अलग Data Types का उपयोग किया जाता है। तब Compiler हमेशा यह Confirm करता है कि Calculation सबसे बड़े Data Type में हो ताकि सटीक (Precise) Result मिले। - Conversion hierarchy (small → large type):
Compiler हमेशा छोटे Type को बड़े Type में Promote करता है। उदाहरण के लिए, int और float के बीच Calculation होगी, तो पहले int को float में बदल दिया जाता है। उसके बाद फिर Operation होता है।
Implicit Type Conversion Example Code
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 10;
float b = 12.5;
float result = a + b; // float + int = float
int res = a + b; // float converted to int (decimal removed)
printf("Float Result = %f\n", result);
printf("Int Result = %d\n", res);
return 0;
}
Output
Float Result = 22.500000
Int Result = 22
Code Working Explanation
इस Program में, दो अलग-अलग Calculation हुई हैं और दोनों में Implicit Conversion का उपयोग हुआ है, लेकिन उनके Result अलग अलग हैं:
1. पहली Calculation: float result = a + b;
- Calculation: a + b (यानी 10 + 12.5)
- Implicit Conversion:
- C Programming के नियम के अनुसार, जब एक int (a=10) और एक float (b=12.5) को जोड़ा जाता है, तो Compiler छोटे Type (int) को बड़े Type (float) में Promote करता है।
- इसलिए, a = 10 अस्थायी रूप से 10.0 float में Compiler बदल देता है।
- जोड़ अब 10.0 + 12.5 = 22.5 के रूप में float में होता है।
- Result का Store होना: चूंकि result वेरिएबल भी float है, इसलिए 22.5 पूरी accuracy के साथ Store हो जाता है।
2. दूसरी Calculation: int res = a + b;
- Calculation: a + b (जोड़ 22.5 ही होता है, जैसा कि ऊपर बताया गया है)।
- Implicit Conversion:
- सबसे पहले, जोड़ (a+b) Hierarchy के कारण float (22.5) में ही होता है (यह Promotion है)।
- अब, इस float Result (22.5) को एक int Variable (res) में Store किया जा रहा है।
- C Language यहाँ फिर से Implicit Conversion करता है—लेकिन यह Demotion (या Narrowing) है!
- float से int में बदलने पर, दशमलव के बाद का सारा Data (यानी 0.5) हटा दिया जाता है (Truncated)।
- Result का Store होना: res एक int Type Variable है इसलिये res Variable में केवल Integer वाला भाग 22 स्टोर होता है, और दशमलव के बाद वाला Data loss हो जाता है।
3.2 Explicit Type Conversion
Explicit Type Conversion को Type Casting भी कहते हैं। यह तब होता है जब हम जानबूझकर और स्पष्ट रूप से (Explicitly) Data Type को बदलने के लिए Code लिखते है।
Syntax:
(target_data_type) expression
कब use करते हैं?
सबसे आम उपयोग Integer Division Problem को हल करना है। जैसे, 5/2 का परिणाम 2 आता है। अगर हमें 2.5 चाहिए, तो हम Explicit Conversion करते हैं।
float result = (float)5 / 2; // result 2.5 होगा
- Data loss possibility:
Explicit Conversion में Data loss होने की संभावना ज़्यादा होती है, खासकर जब हम double या float को int में बदलते हैं (दशमलव हिस्सा हट जाता है)। - Practical C examples:
double को int में बदलना: int value = (int)10.75; (यहां value 10 हो जाएगी)।
Explicit Type Conversion Example Code
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 3;
float result1 = a / b; // integer division (3)
float result2 = (float)a / b; // float division (3.3333)
printf("Without Casting = %f\n", result1);
printf("With Casting = %f\n", result2);
return 0;
}
Output (आउटपुट)
Without Casting = 3.000000
With Casting = 3.333333
Code Working Explanation
इस Program में दो अलग-अलग Division Operation हुए हैं, और उनका परिणाम C Language में Data Conversion नियमों के कारण अलग-अलग आया है:
1. पहली Calculation: float result1 = a / b;
- Calculation : a / b (यानी 10 / 3)
C Programming में, जब हम एक int को दूसरे int से भाग देते हैं, तो ऑपरेशन Integer Division ही होता है। यह Conversion नहीं होता है।
- भागफल (Quotient): 10 / 3 का Integer result 3 आता है। दशमलव के बाद का हिस्सा (0.333…) हटा दिया जाता है (Truncated)।
अब इस int Result 3 को एक float Variable (result1) में Store किया जाता है। यहाँ Implicit Conversion होता है, जहाँ 3 को 3.0 में बदल दिया जाता है।
इसलिए, result1 का मान 3.000000} आता है, जो गलत है।
2. दूसरी Calcultaion: float result2 = (float)a / b;
- Calculation: (float)a / b
- Explicit Conversion (Type Casting):
- यहां हमने जानबूझकर a को Explicitly (float) में Convert किया। अब a की वैल्यू 10.0 (float) है।
- Implicit Conversion (Promotion):
- अब ऑपरेशन है: 10.0 / 3
- यहाँ Compiler Implicit Conversion करता है: छोटे Type (b = 3 int) को बड़े Type (float) में Promote करता है।
- 3 अस्थायी रूप से 3.0 (float) बन जाता है।
- भागफल: अब भाग Float Division के रूप में होता है: 10.0 / 3.0 = 3.333333।
- परिणाम: यह Accurate Result result2 में Store होता है।
3. Implicit Conversion Example In C
| Example No. | Code | Output | Explanation |
| 1. int → float | int i = 5; float f = 2.0; float result = i + f; | 7.0 | int को अपने आप float (5.0) में convert किया गया ताकि Result float में निकले। |
| 2. char → int (ASCII) | char c = ‘A’;int i = 1; int result = c + i; | 66 | ‘A’ की ASCII value 65 होती है। Calculation में char अपने आप 65 बन गया → 65 + 1 = 66 |
| 3. float → double | float x = 5.5f; double y = x; | 5.5 | float को assign करते समय वह अपने आप double में promote हो जाता है। |
| 4. int → double (Promotion) | int a = 10; double b = a; | 10.0 | छोटे type int को बड़ा type double में अपने आप convert कर दिया गया। |
| 5. short → int (Default promotion) | short s = 100; int x = s + 20;\n | 120 | Arithmetic में short हमेशा int में promote होता है। |
4. Explicit Conversion Example In C
| Example No. | Code | Output | Explanation |
| 1. float → int (data loss) | float f = 10.99f; int i = (int)f; | 10 | दशमलव का हिस्सा (.99) पूरी तरह हट गया → data loss। |
| 2. double → int | double d = 25.456; int x = (int)d; | 25 | बड़े type double को छोटे int में force किया गया → precision loss। |
| 3. char → float | char c = ‘b’; float f = (float)c; | 98.00 | ‘b’ की ASCII value (98) को float में cast किया गया। |
| 4. long → int (narrowing) | long value = 5000000000; int x = (int)value; | Undefined / Garbage | int इतनी बड़ी value store नहीं कर सकता → dangerous narrowing conversion। |
| 5. double → char | double d = 67.89;char ch = (char)d; | ‘C’ | 67.89 को cast किया → 67 → ASCII = ‘C’। दशमलव और बड़ा हिस्सा दोनों हट गए। |
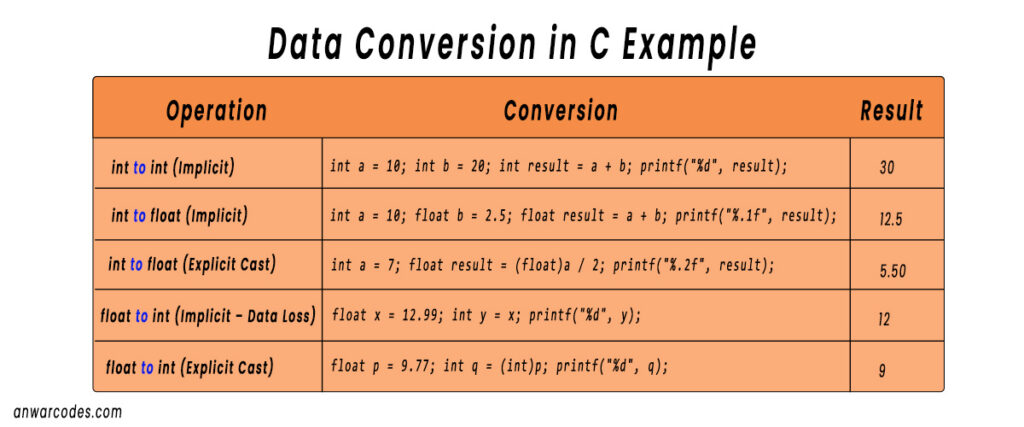
5. Data Conversion में Common Mistakes
- Incorrect parentheses: Type Casting करते समय कोष्ठक () लगाना भूल जाना।
- Unintentional implicit conversion: बिना सोचे-समझे अलग Data Types को मिलाना, जिससे Compiler Unwanted Conversion कर देता है।
- Integer division problem: हमेशा याद रखें, int / int का रिजल्ट हमेशा int ही होगा, भले ही आप उसे float में स्टोर करें (e.g., float f = 5/2; f फिर भी 2.0 होगा)। Type Casting हमेशा ऑपरेटर से पहले होना चाहिए।
- Precision loss in floating values: float से int में बदलने पर दशमलव हिस्सा खो देना।
- Overflow / underflow cases: एक बड़े Type की Value जब छोटे Type की Range से बाहर हो जाती है।
6. Data Conversion In C Quizzes
Q1. Implicit Conversion किस दिशा में होती है?
A) बड़े से छोटे type B) हमेशा int में C) छोटे से बड़े type D) हमेशा float में
Q2. इस code का output क्या होगा?
int a = 5;
float b = 2.5;
float result = a + b;
printf("%f", result);
A) 7.5 B) 5.0 C) 2.5 D) Error
Q3. Explicit Conversion को और किस नाम से जाना जाता है?
A) Promotion B) Auto Conversion C) Data Expansion D) Type Casting
Q4. (int)10.99 का result क्या होगा?
A) 10 B) 11 C) 10.99 D) Error
Q5. इस expression में conversion का प्रकार क्या है?
char c = 'A';
int x = c + 1;
A) Explicit B) कोई conversion नहीं C) Undefined D) Implicit
Q6. float result = 5/2; output क्या होगा?
A) 2.5 B) 5.0 C) 2.0 D) Error
Q7. float result = (float)5/2; सही output क्यों देता है?
A) दोनों operands integer हो जाते हैं B) दोनों operands float हो जाते हैं C) Casting update रोकता है D) कोई conversion नहीं होता
7. FAQs
Q1. C में implicit और explicit conversion में क्या फर्क है?
Ans: Implicit Conversion अपने-आप (automatically) होता है और data loss से बचने की कोशिश करता है।
Explicit Conversion (type casting) programmer जानबूझकर करता है और इसमें data loss का खतरा ज़्यादा होता है।
Q2. क्या type casting से data loss हो सकता है?
Ans: हाँ, खासकर float/double जैसे बड़े type को int जैसे छोटे type में convert करने पर decimal part truncate होकर गायब हो जाता है।
Q3. क्या char हमेशा integer में convert होता है?
Ans: हाँ, char को हमेशा उसकी ASCII integer value के रूप में treat किया जाता है।
इसी वजह से char आसानी से integer में convert हो जाता है।
Q4. Integer division में गलत output क्यों आता है?
Ans: क्योंकि दो integers के division में decimal हिस्सा truncate कर दिया जाता है।
सही result पाने के लिए कम से कम एक operand को float में cast करना पड़ता है।
Q5. क्या float से int conversion safe है?
Ans: नहीं, यह safe नहीं है क्योंकि decimal part पूरी तरह loss हो जाता है।
इसे narrowing conversion कहा जाता है, इसलिए इसे करते समय extra सावधानी चाहिए।
8. Conclusion
इस पूरे article में आपने सीखा कि C Language में Data Conversion कैसे काम करता है और compiler किस logic के आधार पर values को एक type से दूसरे type में बदलता है। आपने समझा कि:
- Implicit Conversion अपने-आप होता है और हमेशा छोटे type को बड़े type में promote किया जाता है, ताकि calculation सुरक्षित रहे।
- Explicit Conversion (Type Casting) programmer खुद करता है और यही सबसे ज़्यादा powerful भी है—लेकिन गलत use करने पर data loss भी हो सकता है।
- Integer division, ASCII conversion, float से int truncation, और mixed-type expressions में conversion कैसे output बदल देता है, यह भी clear हुआ।
- FAQs और examples में practically दिखाया गया कि compiler कैसे सोचता है और हमें कहाँ सावधानी रखनी चाहिए।
- Quizzes ने आपकी understanding को test किया ताकि concept दिमाग में मजबूत बैठ जाए।
अब आपके पास C language में data conversion का पूरा foundation है—जिससे आप हर calculation को confidently लिख सकें, debug कर सकें, और गलत outputs से बच सकें। यह concept आगे pointer arithmetic, expressions, memory, और advanced C programs में बहुत काम आएगा।
