C में Data Type क्या होता है?
C में Data Type ये बताता है कि किसी variable में किस तरह का डेटा रखा जाएगा, और वो memory में कितनी जगह लेगा।
हर variable का एक type होता है — जैसे number, character, या कोई और complex data।
Table of Contents
Example:
- int → पूरा number (जैसे 10, 100)
- float → decimal वाला number (जैसे 3.14)
- char → एक letter (जैसे ‘A’)
C एक statically typed language है — यानी variable का data type use करने से पहले बताना ज़रूरी होता है।
✳ उदाहरण
int age = 25;
float weight = 60.5;
char grade = 'A';इन examples में हमने बताया कि हर variable किस तरह का data रखेगा।
Data Type की ज़रूरत क्यों होती है?
Definition:
Data type से compiler को यह पता चलता है कि variable में कैसा data store होगा, उस पर कौन से operations किए जा सकते हैं और उसे memory में कितना space देना है।
फायदे:
- सही memory allocation होता है
- Code efficient बनता है
- Type-related errors compile time पर पकड़ में आ जाती हैं
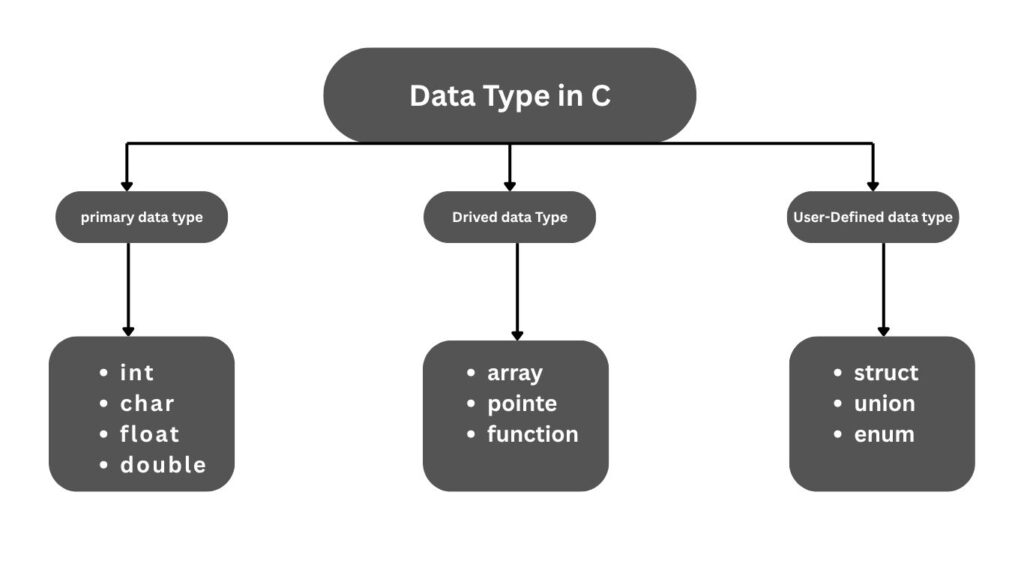
C में Data Types के प्रकार
Definition:
C में data types को चार categories में बाँटा गया है, ताकि हर तरह के data को manage किया जा सके।
Categories:
- Primary (Basic) → बेसिक types जैसे int, char
- Derived → arrays, pointers, functions से बने types
- User-defined → user द्वारा बनाए गए types जैसे struct, union
- Enumeration (enum) → fixed नामों के constants
1. Primary Data Types (बेसिक प्रकार)
Definition:
Primary या Basic data types वो होते हैं जो C के built-in types हैं और जिनसे हर program की शुरुआत होती है।
Types और Details:
| Data Type | मतलब (आसान भाषा में) | Size | Format | Example |
| int | पूरे numbers रखने के लिए | 4 bytes | %d | int a = 10; |
| float | decimal numbers (कम precision) | 4 bytes | %f | float pi = 3.14; |
| double | ज्यादा accurate decimal | 8 bytes | %lf | double d = 3.14159; |
| char | एक अक्षर के लिए | 1 byte | %c | char grade = ‘A’; |
Special Purpose Data Type – void
Definition:
void data type का मतलब होता है “कुछ नहीं”।
इसका use तब होता है जब कोई function कोई value return नहीं करता।
void greet() {
printf("Hello!");
}void को variable के type के रूप में नहीं use किया जा सकता।
Practical Examples
int age = 25;
printf("Age: %d", age);
float temperature = 36.6;
printf("Temp: %.1f", temperature);
double pi = 3.1415926535;
printf("Pi: %.10lf", pi);
char grade = 'A';
printf("Grade: %c", grade);
2. Derived Data Types
Definition:
Derived data types वो होते हैं जो existing data types से मिलकर बनते हैं — जैसे array, pointer, और function।
| Type | क्या करता है | Example |
| Array | एक जैसे data का group बनाता है | int arr[5]; |
| Pointer | किसी variable का memory address रखता है | int *ptr = &a; |
| Function | reusable काम करने वाला code block | int sum(int a, int b); |
Example:
int add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
int main() {
int arr[3] = {10, 20, 30};
int *ptr = arr;
printf("First: %d\n", arr[0]);
printf("Pointer: %d\n", *(ptr + 1));
printf("Sum: %d\n", add(arr[0], arr[1]));
return 0;
}
3. User-Defined Data Types
Definition:
User-defined types वो होते हैं जिन्हें programmer खुद define करता है — ताकि complex data को structure में रखा जा सके।
| Type | क्या करता है | Example |
| struct | अलग-अलग types को group करता है | struct Student |
| union | same memory पर कई members रखता है | union Data |
| typedef | किसी type को नया नाम देता है | typedef int Marks; |
| enum | कुछ fixed नामों वाले constants बनाता है | enum Day |
Examples:
struct Student {
int roll;
char name[50];
float marks;
};
union Data {
int i;
float f;
};
Enum – Fixed Options
Definition:
enum का use तब होता है जब आपको एक ही category के multiple नामों वाले values define करने हों — जैसे दिन, रंग, स्टेटस।
Examples:
enum Day { Sunday, Monday, Tuesday };
enum Day today = Monday;
printf("Day: %d", today);
enum TrafficLight { RED, YELLOW, GREEN };
int main() {
enum TrafficLight signal = GREEN;
switch(signal) {
case RED: printf("Stop\n"); break;
case YELLOW: printf("Get Ready\n"); break;
case GREEN: printf("Go\n"); break;
}
return 0;
}
4. Modifiers in C
Definition:
Modifiers variables की range, size, और sign को control करते हैं। इन्हें basic data types के साथ जोड़कर use किया जाता है।
| Modifier | मतलब |
| signed | Positive और Negative values |
| unsigned | सिर्फ Positive values |
| short | कम memory use करता है |
| long | बड़ी range देता है |
| long long | बहुत बड़ी range देता है |
Example:
unsigned int age = 25;
signed int balance = -500;
short int x = 100;
long long int bigValue = 1234567890123LL;Memory Size Table (Approx.)
| Type | 32-bit Size | 64-bit Size | Range |
| short int | 2 bytes | 2 bytes | –32,768 to +32,767 |
| unsigned short | 2 bytes | 2 bytes | 0 to 65,535 |
| int | 4 bytes | 4 bytes | –2.1B to +2.1B |
| unsigned int | 4 bytes | 4 bytes | 0 to 4.2B |
| long int | 4 bytes | 8 bytes | Depends on system |
| long long int | 8 bytes | 8 bytes | –9 quintillion to +9 quintillion |
Common Mistakes
unsigned int x = -5; // ❌ गलत: unsigned में negative value नहीं चलेगी
int x = -5; // ✅ सही
Important Notes (आसान भाषा में)
- हर variable का type पहले से बताना ज़रूरी है
- C में default number type = int
- Memory size system पर depend करता है
- char के पीछे ASCII value छिपी होती है
- float और double में accuracy का फर्क होता है
- Modifiers से आप performance और memory दोनों बेहतर बना सकते हैं
- struct = कई variables एक जगह
- union = सभी variables एक ही memory use करते हैं
- array = एक जैसे items का fixed group
- pointer = powerful है लेकिन risk के साथ आता है
- void pointer किसी भी type को point कर सकता है लेकिन cast करना जरूरी है
Conclusion
C language में data types की समझ बहुत ज़रूरी है। इससे:
- Memory का सही use होता है
- Program efficient और error-free बनता है
- Code readable और maintainable होता है
अगर आप programming सीख रहे हैं या किसी technical interview की तैयारी कर रहे हैं, तो data types की mastery आपकी foundation मजबूत करेगी।
