जब हम C Programming सीखते हैं, तो एक ऐसा concept सामने आता है जो data को एक साथ store करने में बहुत काम आता है — उसे कहते हैं Array.
अगर आप beginner हैं, तो “C Language Array क्या है?”, “क्यों ज़रूरी है?”, और “कैसे काम करता है?” – ये सारे सवाल आज इस पोस्ट में step-by-step clear हो जाएंगे।
Table of Contents
1. Array क्या होता है?
C Language में Array एक ऐसा variable होता है जो एक ही data type के कई values को एक साथ store करने की सुविधा देता है।
अगर हमें 10 students के marks store करने हैं, तो हमें 10 अलग-अलग variables बनाने होंगे, जैसे:
int m1, m2, m3, m4, m5, m6, m7, m8, m9, m10;
ये तरीका झंझट वाला है।
लेकिन array की मदद से बस एक variable में सारे marks store किए जा सकते हैं:
int marks[10];
अब marks[0] से लेकर marks[9] तक में students के marks रख सकते हैं।
यानी array हमें multiple data values को efficiently manage करने की ताकत देता है।
2. Array क्यों इतना Useful है?
हमारे मन में अक्सर ये सवाल उठता हैं — जब हम अलग-अलग variable बना सकते हैं तो array की क्या जरूरत क्यों ?
यहाँ कुछ reasons हैं जिनसे समझो क्यों C language में array इतना जरूरी concept है:
- Memory Management आसान हो जाता है —क्योंकि array में सारे समान type के data एक-दूसरे के पास memory में store होते हैं।
- Code छोटा और readable बनता है — बार-बार variables declare नहीं करने पड़ते।
- Data पर operations आसान होते हैं — loops के ज़रिए पूरे array पर एक साथ calculation किये जा सकते हैं।
- Sorting, Searching जैसी प्रक्रिया आसान होती है — array के साथ algorithm लगाना simple हो जाता है।
Real Life Example:
जैसे एक स्कूल में हर student का roll number और marks एक register में लिखा जाता है —
वैसे ही array एक “register” है जो related data को एक जगह रखता है।
3. Array का Declaration और Initialization
Declaration
Array declare करने का basic syntax है:
data_type array_name[size];
उदाहरण:
int marks[5];
यहाँ int data type है, marks array का नाम है, और [5] size है, इसका मतलब है इसमें 5 elements store हो सकते हैं।
Initialization
Array को values assign करने के दो तरीके हैं:
1️. Declaration के समय:
int marks[5] = {80, 70, 65, 90, 85};
2️. Declaration के बाद:
marks[0] = 80;
marks[1] = 70;
marks[2] = 65;
marks[3] = 90;
marks[4] = 85;
लेकिन अगर हम initialize करते समय size नहीं देते:
int marks[] = {80, 70, 65, 90, 85};
तो compiler अपने आप size 5 मान लेगा।
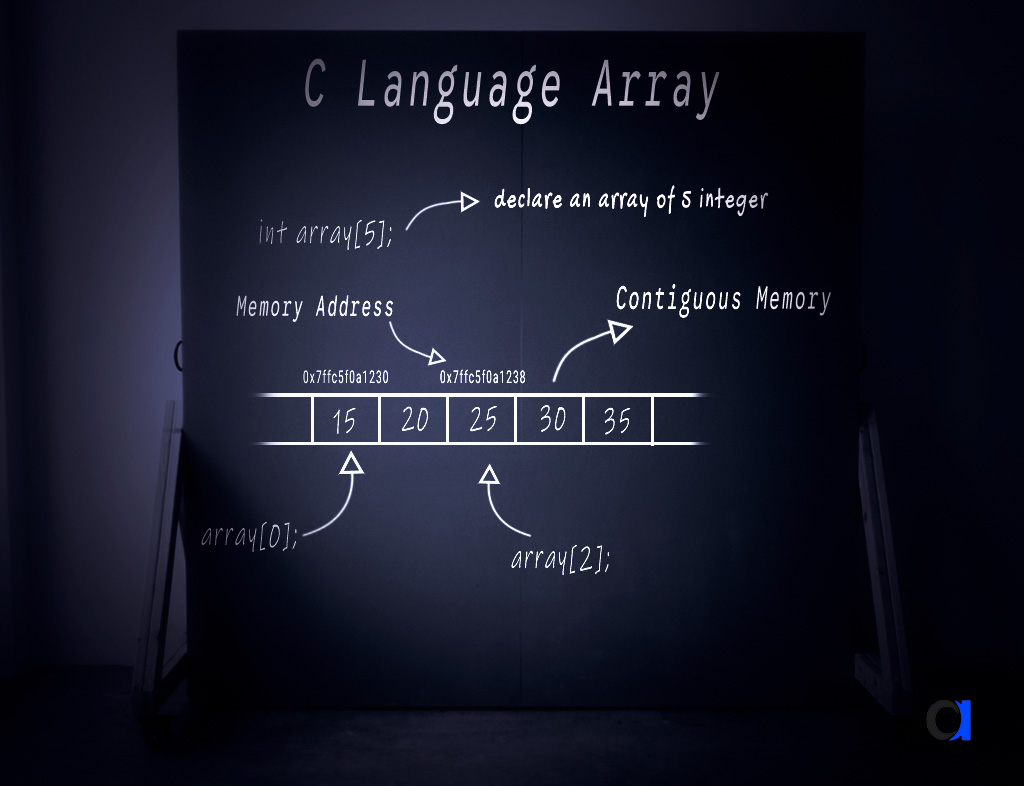
4. Array के Elements को Access कैसे करें?
Array के हर element को access करने के लिए index number का उपयोग किया जाता है।
Index हमेशा 0 से शुरू होता है।
उदाहरण:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int marks[] = {80, 70, 65, 90, 85};
printf("Marks of first student: %d\n", marks[0]);
printf("Marks of third student: %d\n", marks[2]);
printf("Marks of fifth student: %d\n", marks[4]);
return 0;
}
Output:
Marks of first student: 80
Marks of third student: 65
Marks of fifth student: 85
5. Array के प्रकार
C language में array के तीन मुख्य प्रकार होते हैं:
1. Single Dimensional Array (1D Array)
यह सबसे basic array होता है, जहाँ data एक row में store होता है।
int marks[5] = {80, 85, 70, 90, 95};
2. Multi Dimensional Array
चलिये 2D array को थोड़ा समझ लेते क्योंकि 2D array ज्यादा use किया जाता है।
2D Array क्या होता है?
2D Array को आप एक table (तालिका) की तरह समझो —
जिसमें rows और columns होते हैं।
हर cell में एक data item रखा जाता है।
उदाहरण:
अगर हमारे पास 3 students के 2 subjects के marks हैं,
तो हम उन्हें इस तरह store कर सकते हैं:
| Student | Subject 1 | Subject 2 |
| 1 | 80 | 85 |
| 2 | 75 | 90 |
| 3 | 88 | 79 |
इसी table को हम 2D array से represent कर सकते हैं।
2D Array की Declaration
data_type array_name[row][column];
उदाहरण:
int marks[3][2];
इसका मतलब — marks एक array है जिसमें
3 rows और 2 columns होंगे → यानी total 3 × 2 = 6 elements.
2D Array Example Program
इस program में हम सीखेंगे कैसे 2D Array में user से element करवायेंगे, और फिर उसे कैसे print करेंगे।
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int marks[3][2]; // 3 students, 2 subjects
int i, j;
printf("Enter marks of 3 students (2 subjects each):\n");
// Taking input
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
printf("Student %d, Subject %d: ", i+1, j+1);
scanf("%d", &marks[i][j]);
}
}
// Displaying output
printf("\nDisplaying entered marks:\n");
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
printf("%d\t", marks[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter marks of 3 students (2 subjects each):
Student 1, Subject 1: 80
Student 1, Subject 2: 85
Student 2, Subject 1: 75
Student 2, Subject 2: 90
Student 3, Subject 1: 88
Student 3, Subject 2: 79
Displaying entered marks:
80 85
75 90
88 79
Program Explanation:
- हमने 2D array marks[3][2] बनाया।
→ इसका मतलब है 3 rows (students) और 2 columns (subjects)। - दो nested for loops का use किया गया —
- Outer loop → rows को handle करता है (students)
- Inner loop → columns को handle करता है (subjects)
- Outer loop → rows को handle करता है (students)
- scanf से marks लिए गए और फिर printf से table की तरह print किया गया।
Important Point:
2D array की memory भी continuous होती है,
लेकिन data को row-wise या column-wise access करने का तरीका depend करता है —
C में data row-major order में store होता है।
3. Character Array (String)
अगर array में characters store किए जाएं, तो उसे character array या string कहते हैं।
char name[] = “AnwarCodes”;
Character array internally ऐसे store होता है:
A | n | w | a | r | C | o | d | e | s |\0
यहाँ \0 null character होता है जो string के end को दर्शाता है।
6. Array और Loop का संबंध
जैसे अभी इससे पहले हमने 2D Array का example देखा, जिसमें for loop की मदद से बड़ी आसानी और कम lines के code में data को input और output कराया गया था।
C language में array और loop का रिश्ता बहुत गहरा है, क्योंकि array में अक्सर कई elements होते हैं जिन्हें manually access करना time-consuming और repetitive हो सकता है।
यही वजह है कि array और loop का combination बेहद powerful माना जाता है।
Loop की मदद से हम array के हर element पर आसानी से कोई भी operation — जैसे addition, searching, या printing — बहुत ही कम कोड में कर सकते हैं।
उदाहरण:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int marks[5] = {80, 85, 70, 90, 95};
printf("Marks of all students:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Student %d: %d\n", i + 1, marks[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Student 1: 80
Student 2: 85
Student 3: 70
Student 4: 90
Student 5: 95
Loop की मदद से array में searching, sorting, और sum जैसी प्रक्रिया करना बहुत आसान हो जाता है।
7. Array पर आधारित कुछ Practical Programs
अब कुछ useful और programs देखते हैं जो C language array को practically समझाते हैं।
Program 1: Array Elements का Sum निकालना
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sum += num[i];
}
printf("Total sum of array = %d", sum);
return 0;
}
Output:
Total sum of array = 150
Program 2: Array में सबसे बड़ा Element ढूंढना
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[5] = {10, 55, 20, 90, 45};
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
printf("The largest number = %d", max);
return 0;
}
Output:
The largest number = 90
Program 3: User से Input लेकर Array में Store करना
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int marks[5];
printf("Enter marks of 5 students:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Student %d: ", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &marks[i]);
}
printf("\nEntered Marks:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Student %d = %d\n", i + 1, marks[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Output (User Input पर निर्भर करेगा)
Enter marks of 5 students:
Student 1: 80
Student 2: 75
Student 3: 90
Student 4: 85
Student 5: 88
Entered Marks:
Student 1 = 80
Student 2 = 75
Student 3 = 90
Student 4 = 85
Student 5 = 88
FAQs – C Language Array से जुड़े सवाल
Q1. Array का size runtime में बदला जा सकता है?
Ans: C में array का size compile-time पर fix होता है। अगर runtime flexibility चाहिए तो pointers और dynamic memory allocation (malloc, calloc) का उपयोग करना चाहिए।
Tip: Beginners पहले static array समझें, फिर dynamic allocation सीखें।
Q2. Mixed data types को एक array में store किया जा सकता है?
Ans: नहीं, C array में केवल same data type के elements store किए जा सकते हैं। अगर अलग types चाहिए तो structure या union use करना चाहिए।
Tip: सही data structure चुनकर data को organize करना सीखें।
Q3. Array और String में क्या अंतर है?
Ans: String C में character array होती है, और इसके end में हमेशा \0 null character होता है।
Tip: Strings को समझना arrays और pointers को समझने का अच्छा step है।
Q4. Array elements को pointer से access किया जा सकता है?
Ans: हाँ, *(arr + i) syntax से किसी element को access किया जा सकता है। arr[i] और *(arr + i) दोनों same location को point करते हैं।
Tip: यह dynamic memory, function pointers और advanced array operations के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
Q5. Array में beginners अक्सर कौन-सी mistakes करते हैं?
Ans: Common mistakes:
- Index out of bound – array के size से बाहर access करना।
- Uninitialized array read करना – हमेशा values assign करें।
- Wrong data type assign करना – Type-safe रहें।
Tip: Debugging और best practices सीखकर इन errors से बचा जा सकता है।
निष्कर्ष (Conclusion)
तो अब आप समझ गए होंगे कि C Language Array क्या है, क्यों जरूरी है, और इसे कैसे use किया जाता है।
Array data को एक structured तरीके से store करने की सबसे basic और efficient technique है।
यह हर beginner के लिए जरूरी concept है क्योंकि बाद में इसी concept पर pointers, structures, strings और dynamic memory allocation जैसे topics निर्भर करते हैं।
अगर आप C language को गहराई से सीखना चाहते हैं, तो array के program practice जरूर करें – जैसे sum, average, max-min, sorting और matrix operations।
Final Note:
“Array programming का foundation है। अगर आपने C language array को अच्छे से समझ लिया, तो आगे advance pointers और data structures सीखना बहुत आसान हो जाएगा।”
