अगर आप C Programming सीख रहे हैं और यह समझना चाहते हैं कि Function क्या होता है, कैसे बनाते हैं, और प्रोग्राम में इसका इस्तेमाल कैसे किया जाता है — तो यह article आपके लिए है।
इस पूरे article के अंत तक, आपको C Programming में Function का हर concept इतनी clarity से समझ आ जाएगा कि आप खुद अपने programs में confidently functions बना पाएंगे।
तो चलिए, step-by-step सीखना शुरू करते हैं।
Table of Contents
1. Function क्या होता है?
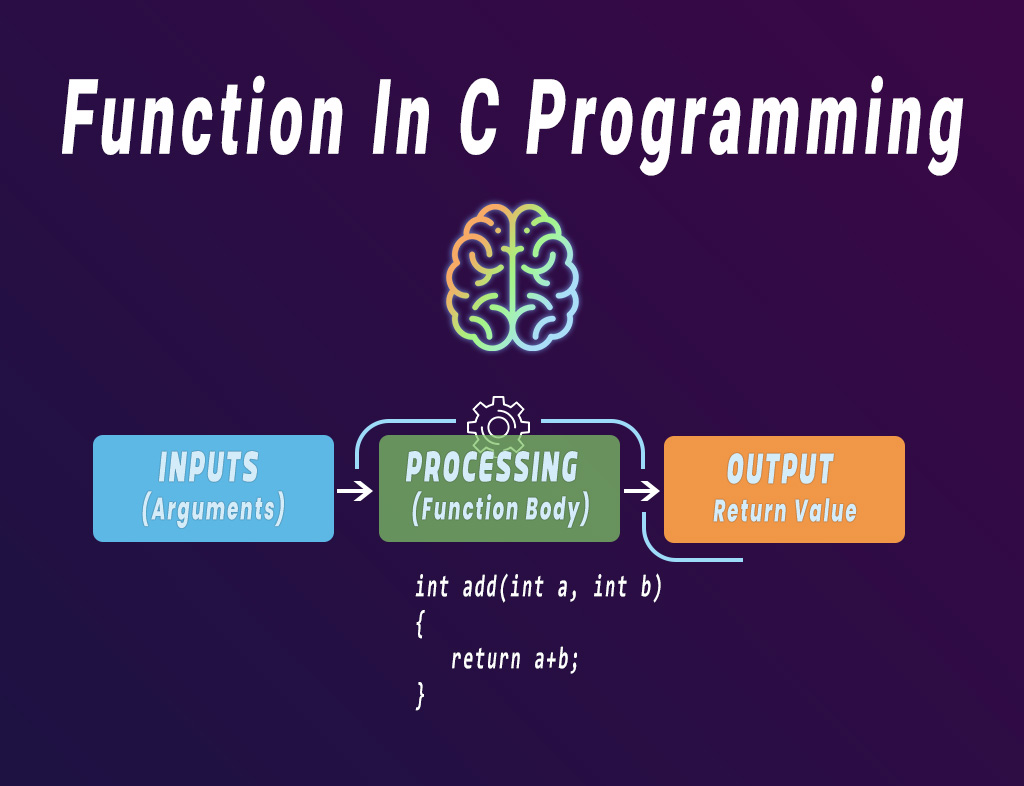
C programming में function एक ऐसा block होता है जो किसी specific task को perform करता है।
इसे हम mini program भी कह सकते हैं जो हमारे main program के अंदर काम करता है।
Simple Function का Example:
#include <stdio.h>
void greet() {
printf("Hello, Welcome to C Programming! By AnwarCodes\n");
}
int main() {
greet(); // Function call
return 0;
}
Output :
Hello, Welcome to C Programming! By AnwarCodes
यहां greet() एक function है जो केवल एक message print करता है।
जब main() में इसे call किया जाता है, तब इसका greet() function का code execute होता है।
आसान शब्दों में:
Function का मतलब होता है — “काम को टुकड़ों में बांटकर करना”
इससे code समझना, maintain करना और debug करना आसान होता है। और same task को दोबारा करने के लिए code rewrite नहीं करना पड़ता।
2. C Programming में Function के प्रकार
1. Library Function (Predefined Function)
ये वो Functions होते हैं जो c programming के library में पहले से बने बनाये होते हैं। जैसे stdio.h, math.h, stdlib.h आदि। हमें इन्हे खुद से define करने की जरुरत नहीं होती बस call करके उपयोग करना होता है। जैसे printf(), scanf() अभी तक हम इस्तेमाल कर रहे हैं। ये library Functions है, जो stdio.h header file में defined है। किसी भी Library function को उपयोग करने से पहले उनकी Header file को Include करना होता है। निचे कुछ function और उनके library दिए हुए है
Example : C Programming में Library Function
निचे कुछ library function दिए गए हैं।
| Library | Functions |
| stdio.h | printf(), scanf(), gets(), puts() etc. |
| math.h | pow(), sqrt() |
| stdlib.h | malloc(), calloc(), realloc() etc. |
निचे दिए गए program में सिर्फ library functions का उपयोग किये गए हैं। जैसे printf(), scanf() और pow() Function इस program में किसी भी number को enter करके calculate कर सकते हैं।
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h> // math.h header file - isme mathematical functions (jaise pow) defined hote hain
// Program to find the power of a number using library functions
int main()
{
int base, exponent;
double result;
// printf() → stdio.h ka library function jo console par message print karta hai
printf("Enter base number: ");
// scanf() → stdio.h ka library function jo user se input leta hai
scanf("%d", &base);
printf("Enter exponent number: ");
scanf("%d", &exponent);
// pow() → math.h ka library function jo base^exponent calculate karta hai
result = pow(base, exponent);
// printf() again result dikhane ke liye
printf("The power of %d raised to %d is %.2f\n", base, exponent, result);
return 0;
}
Output :
Enter base number: 12
Enter exponent number: 2
The power of 12 raised to 2 is 144.00
3. User Defined Function
User Defined Function वो functions होते है , जो Programmer खुद बनाते हैं। अगर हमारे जरुरत के हिसाब से कोई function c library में नहीं है। तो हम खुद बनाते हैं। जिसे User defined function कहते है।
निचे addition का program दिया गया हैं जो दो number जोड़कर return करता हैं। इस program में addNumbers() एक User-Defined Function है।
#include <stdio.h>
// Function declaration with parameters
int addNumbers(int a, int b) {
return a + b; // दोनों numbers को जोड़कर return कर रहा है
}
int main() {
int num1, num2, sum;
printf("Enter first number: ");
scanf("%d", &num1);
printf("Enter second number: ");
scanf("%d", &num2);
// Function call with arguments
sum = addNumbers(num1, num2);
printf("Sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter first number: 20
Enter second number: 10
Sum = 30
Output:
Sum = 15
4. C Programming में Function का Structure
C programming में function का एक fixed structure होता है:
return_type function_name(parameter_list) {
// function body
}
Parts Explanation:
| Part | Meaning |
| return_type | Function क्या return करेगा (जैसे int, float, void आदि) |
| function_name | Function का नाम |
| parameter_list | Function को दी जाने वाली values Recive करने वाला variable |
| function body | Actual code जो body में लिखा होता है, जो function call के समय execute होता है |
Example:
int multiply(int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
5. Function Declaration, Definition और Call
C Programming में function को use करने से पहले उसका declaration ज़रूरी होता है।
1. Declaration (Prototype)
Compiler को बताता है कि function कैसा दिखेगा है।
int add(int, int);
2. Definition
Function का actual code जो body में होता है।
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
3. Function Call
जहां हम function को call करते हैं, जब हम function को call करते हैं तब function body के अंदर का code execute होता है। जैसे निचे एक छोटा सा example दिया गया है।
#include <stdio.h>
// यह function दो integers को add करता है और उनका योग (sum) return करता है
int add(int num1, int num2)
{
// num1 और num2 को जोड़कर result return किया जाता है
return (num1 + num2);
}
int main()
{
int result;
// add() function को call किया गया है और 10 तथा 20 arguments के रूप में दिए गए हैं
result = add(10, 20);
// Result को print किया जा रहा है
printf("Addition 10 + 20 = %d", result);
return 0;
}
Output:
Addition 10 +20 = 30
6. Function Parameters और Arguments
Parameters वो variables होते हैं जो function को input लेने में मदद करते हैं।
Arguments वो actual values होती हैं जो function call के समय function को भेजी जाती हैं।
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
// Function prototype (compiler को पहले से बता देता है कि greet() नाम का function exist करता है)
void greet(char Name[]);
int main()
{
// greet() function को call किया गया और "AnwarCodes" argument के रूप में भेजा गया
greet("AnwarCodes");
return 0;
}
// Function definition
// यह function एक string (character array) को input के रूप में लेता है और उसे print करता है
void greet(char Name[])
{
// Name array में जो string है उसे print किया जाता है
printf("%s", Name);
}
Output:
AnwarCodes
यहां “AnwarCode” argument है, और char name[] parameter है।
हर function कुछ न कुछ return कर सकता है — integer, float, character या कुछ भी नहीं (void)
7. Function के प्रकार Based on Argument और Return Value
C programming में function को उनके return value (input value) और argument के आधार पर 4 category में बांटा गया है। निचे सभी function के example program दिए गए हैं।
1.Function Without argument and without return Value
इस type के function में कोई input नहीं लिया जाता और कोई value return नहीं की जाती।
Function खुद ही अपना काम करता है।
Example :
#include <stdio.h>
// Function definition - बिना argument और बिना return
void displayMessage() {
printf("Hello! This is a function without arguments and without return value.\n");
}
int main() {
// Function call
displayMessage();
return 0;
}
Output:
Hello! This is a function without arguments and without return value.
2. Function With argument but without return Value
इस type के function में input arguments लिए जाते हैं, लेकिन कोई value return नहीं होती।
ये सिर्फ काम perform करता है और result सीधे print करता है।
Example :
#include <stdio.h>
// Function definition - argument है लेकिन return value नहीं है
void printSum(int a, int b) {
printf("Sum = %d\n", a + b);
}
int main() {
int x, y;
printf("Enter two numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
// Function call with arguments
printSum(x, y);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter two numbers: 30
20
Sum = 50
3. Function Without argument but return Value
इस type के function में input arguments नहीं लिए जाते हैं लेकिन value return की जाती है।
Example :
#include <stdio.h>
// Function definition - argument नहीं है लेकिन return value है
int getNumber() {
int num;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
return num; // input किया हुआ number return कर रहा है
}
int main() {
int n;
// Function call
n = getNumber();
printf("You entered: %d\n", n);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter a number: 22
You entered: 22
4. With argument and with return Value
इस type के function में input arguments भी लिए जाते हैं और value return भी की जाती है।
ये सबसे useful और commonly used function है।
Example :
#include <stdio.h>
// Function definition - argument और return value दोनों हैं
int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b; // दोनों numbers को multiply करके return कर रहा है
}
int main() {
int x, y, result;
printf("Enter two numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
// Function call with arguments and return value
result = multiply(x, y);
printf("Multiplication = %d\n", result);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter two numbers: 10
5
Multiplication = 50
8. C Programming में Function का Real Example Program
निचे एक Real Life use के लिए एक Common Unit conversion Program दिया गया हैं। जिससे आपको अच्छे से समझने में मदद करेगा।
#include <stdio.h>
// Function declarations (prototypes)
void lengthConversion();
void weightConversion();
void temperatureConversion();
void timeConversion();
int main()
{
int choice;
do
{
// Main menu for user
printf("=====================================\n");
printf(" Unit Conversion Program \n");
printf("=====================================\n");
printf("Choose the conversion type:\n");
printf("1.Length\n");
printf("2.Weight\n");
printf("3.Temperature\n");
printf("4.Time\n");
printf("0.Exit\n");
printf("Enter your choice (1-4): ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
// Switch-case to call the respective conversion function
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
lengthConversion(); // Call length conversion function
break;
case 2:
weightConversion(); // Call weight conversion function
break;
case 3:
temperatureConversion(); // Call temperature conversion function
break;
case 4:
timeConversion(); // Call time conversion function
break;
case 0:
printf("Exiting the program.\n"); // Exit message
break;
default:
printf("Invalid main choice!\n"); // Invalid input handling
}
} while (choice != 0); // Loop until user enters 0
return 0;
}
// Function for Length Conversion
void lengthConversion()
{
int lenChoice;
float value, convertedValue;
printf("Length Conversion:\n");
printf("1.Meters to Feet\n");
printf("2.Feet to Meters\n");
printf("Enter your choice (1-2): ");
scanf("%d", &lenChoice);
if (lenChoice == 1)
{
// Formula: 1 meter = 3.28084 feet
printf("Enter length in meters: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = value * 3.28084;
printf("%.2f meters is %.2f feet\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else if (lenChoice == 2)
{
// Formula: 1 foot = 0.3048 meter
printf("Enter length in feet: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = value / 3.28084;
printf("%.2f feet is %.2f meters\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else
{
printf("Invalid choice for length conversion.\n");
}
}
// Function for Weight Conversion
void weightConversion()
{
int weightChoice;
float value, convertedValue;
printf("Weight Conversion:\n");
printf("1.Kilograms to Pounds\n");
printf("2.Pounds to Kilograms\n");
printf("Enter your choice (1-2): ");
scanf("%d", &weightChoice);
if (weightChoice == 1)
{
// Formula: 1 kilogram = 2.20462 pounds
printf("Enter weight in kilograms: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = value * 2.20462;
printf("%.2f kilograms is %.2f pounds\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else if (weightChoice == 2)
{
// Formula: 1 pound = 0.453592 kilogram
printf("Enter weight in pounds: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = value / 2.20462;
printf("%.2f pounds is %.2f kilograms\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else
{
printf("Invalid choice for weight conversion.\n");
}
}
// Function for Temperature Conversion
void temperatureConversion()
{
int tempChoice;
float value, convertedValue;
printf("Temperature Conversion:\n");
printf("1.Celsius to Fahrenheit\n");
printf("2.Fahrenheit to Celsius\n");
printf("Enter your choice (1-2): ");
scanf("%d", &tempChoice);
if (tempChoice == 1)
{
// Formula: (°C × 9/5) + 32 = °F
printf("Enter temperature in Celsius: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = (value * 9 / 5) + 32;
printf("%.2f Celsius is %.2f Fahrenheit\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else if (tempChoice == 2)
{
// Formula: (°F − 32) × 5/9 = °C
printf("Enter temperature in Fahrenheit: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = (value - 32) * 5 / 9;
printf("%.2f Fahrenheit is %.2f Celsius\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else
{
printf("Invalid choice for temperature conversion.\n");
}
}
// Function for Time Conversion
void timeConversion()
{
int timeChoice;
float value, convertedValue;
printf("Time Conversion:\n");
printf("1.Hours to Minutes\n");
printf("2.Minutes to Hours\n");
printf("Enter your choice (1-2): ");
scanf("%d", &timeChoice);
if (timeChoice == 1)
{
// Formula: 1 hour = 60 minutes
printf("Enter time in hours: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = value * 60;
printf("%.2f hours is %.2f minutes\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else if (timeChoice == 2)
{
// Formula: 1 minute = 1/60 hour
printf("Enter time in minutes: ");
scanf("%f", &value);
convertedValue = value / 60;
printf("%.2f minutes is %.2f hours\n", value, convertedValue);
}
else
{
printf("Invalid choice for time conversion.\n");
}
}
Output:
Choose the conversion type:
1.Length
2.Weight
3.Temperature
4.Time
0.Exit
Enter your choice (1-4): 1
Length Conversion:
1.Meters to Feet
2.Feet to Meters
Enter your choice (1-2): 2
Enter length in feet: 12
12.00 feet is 3.66 meters
C Programming में Function के कुछ Important FAQS
Q1. Function क्या होता है C में?
Ans: Function C language का एक block होता है जो कोई specific task perform करता है। यह code को modular, reusable, और easy to manage बनाता है।
Example:
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}Tip: हर बड़ा program छोटे functions में divide करना best practice माना जाता है।
Q2. C में कितने प्रकार के functions होते हैं?
Ans: C में functions दो प्रकार के होते हैं:
- Library functions — जैसे
printf(),scanf(),sqrt()आदि। - User-defined functions — जो programmer खुद define करते है, जैसे
add(),greet()आदि।
Tip: Library functions ready-made होते हैं जबकि user-defined functions custom logic के लिए बनाए जाते हैं।
Q3. Function prototype क्या होता है और यह जरूरी क्यों है?
Ans: Function prototype compiler को बताता है कि function का नाम, return type और parameters क्या हैं।
Example:
int add(int, int); // Function prototypeTip: Function prototype लिखने से compiler को function के बारे में पहले से पता चलता है और warnings से बचा जा सकता है।
Q4. Function को call करने के कितने तरीके हैं?
Ans: Function को call करने के दो तरीके होते हैं:
- Call by Value: Actual value copy होकर parameter में जाती है (most common method)।
- Call by Reference: Actual variable का address भेजा जाता है (pointers के माध्यम से)।
Tip: जब function को original variable बदलना हो तो Call by Reference use करें।
Q5. Function का return type क्या होता है?
Ans: Return type बताता है कि function कौन सी type की value return करेगा — जैसे int, float, char, या void।
Example:
int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b; // int value return करता है
}Tip: अगर function कुछ return नहीं करता तो उसका return type void होता है।
Conclusion (निष्कर्ष)
C programming में function एक powerful feature है जो program को छोटे-छोटे manageable parts में divide करता है। Function use करने से code readable, reusable aur maintainable बनता है।
इस article में हमने सीखा:
- Function ka syntax (return type, name, parameters aur body).
- Function ke parts – prototype, declaration, definition aur call.
- Function ke types – arguments aur return value ke base par चार categories.
- Example programs jisme parameters aur return type ka actual use दिखाया गया।
- C programming में function ke kuchh topic बाकी हैं , जो pointer वाले पोस्ट पढ़ेंगे। जैसे Call by Reference.
जब हम large program लिख रहे हो तो functions usse easy और organized बना देते हैं। यही वजह है कि C programming में function को modular programming का base माना जाता है।
Suggetion :
कोई भी skill सिर्फ पढ़ने या देखने से नहीं आती, जब तक उसकी practice न की जाए। खासकर programming में – जितना ज़्यादा आप practice करेंगे, उतना ही ज़्यादा फायदा मिलेगा।
